In today’s fast-moving industries, warehouse space management is more than just organizing storage — it’s a strategic pillar of operational efficiency.
In construction, manufacturing, logistics, and retail, warehouse optimization defines how smoothly materials flow, how quickly projects are completed, and how profitably operations run.
A poorly managed warehouse leads to idle inventory, blocked capital, and project delays. In contrast, an optimized warehouse ensures seamless material movement, better storage efficiency, and faster retrieval — saving time, cost, and space.
This guide explores proven strategies, technologies, and KPIs that help you transform your warehouse into a smart, data-driven, and high-performance asset.
The Strategic Importance of Warehouse Space Management
Optimizing your warehouse isn’t only about neat storage — it’s about maximizing space utilization, reducing handling time, and improving visibility across every stock item.
Common Challenges in Warehouse Optimization
- Underutilized or overcrowded storage areas
- Long picking and retrieval times
- Overstocking or stockouts of key materials
- Poor real-time inventory control
- Safety and accessibility issues
Benefits of Optimized Warehouse Space
- Lower carrying costs
- Faster material retrieval
- Improved order accuracy
- Higher safety and compliance standards
When you apply effective warehouse space management, every square foot adds value to your operations.

Assessing Your Current Warehouse Layout
Before improving space utilization, analyze your existing warehouse layout and workflow.
Key Areas to Audit
- Space Utilization Rate: Aim for 85–90% utilization for optimal flow.
- Material Flow: Track movement from receiving → storage → dispatch.
- Travel Time: Measure time spent on picking and replenishment.
- Bottlenecks: Identify areas of congestion or delay.
- Safety & Accessibility: Ensure aisles and zones follow ergonomic standards.
A detailed audit every 6–12 months keeps warehouse performance aligned with changing demand.
Space Optimization Techniques for Modern Warehouses
- Vertical Storage Solutions
Use vertical racking, mezzanine floors, and automated carousels to maximize vertical space without costly expansion.
- Smart Zoning
Organize zones by:
-
- Frequency of use (fast-moving goods near dispatch)
- Material type (hazardous, fragile, or heavy)
- Temperature requirements (cold or climate-controlled areas)
- Cross-Docking Operations
Cross-docking allows materials to move directly from inbound to outbound without storage delays — improving inventory turnover and reducing costs.
- FIFO and LIFO Methods
Apply FIFO (First In, First Out) for perishable goods and LIFO (Last In, First Out) when retrieval speed matters more than rotation.
- Slotting Optimization
Use analytics to assign optimal storage locations based on item size, frequency, and handling needs. This boosts retrieval speed and labor efficiency.
Advanced Stock Management Strategies
The core of effective warehouse space management lies in accurate, real-time inventory control.
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Use barcodes, RFID, or IoT sensors to maintain live inventory visibility and avoid over-ordering.
- ABC Analysis
- A Items: High value, strict monitoring
- B Items: Moderate value, regular tracking
- C Items: Low value, automated handling
- Safety Stock & Reorder Points
Set dynamic reorder levels based on lead time and usage to avoid stockouts without overstocking.
- WMS and ERP Integration
Integrate your Warehouse Management System (WMS) with ERP tools to achieve end-to-end visibility across procurement, dispatch, and billing.
Leveraging Technology: Building a Smart Warehouse
Modern smart warehouses rely on automation, data, and AI for better decision-making.
- Warehouse Management System (WMS)
A WMS automates space allocation, picking routes, and inventory tracking while improving accuracy and reducing human error.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices track temperature, shelf weight, and equipment usage, enabling proactive maintenance and better space management.
- Robotics & Automation
AGVs, conveyors, and robotic pickers improve retrieval times and minimize labor costs.
- Predictive Analytics & AI
AI tools use demand patterns to forecast inventory needs, reducing waste and improving inventory turnover ratios.
Space Utilization, Safety & Compliance
Optimized warehouse space management must balance efficiency with safety.
Key Safety Measures
- Maintain minimum 3.5 ft aisles
- Use anti-slip flooring and rated shelves
- Label load capacities
- Install alarms and fire safety systems
- Conduct regular drills and audits
Compliance with ISO 45001 and OSHA ensures safety and minimizes liability.
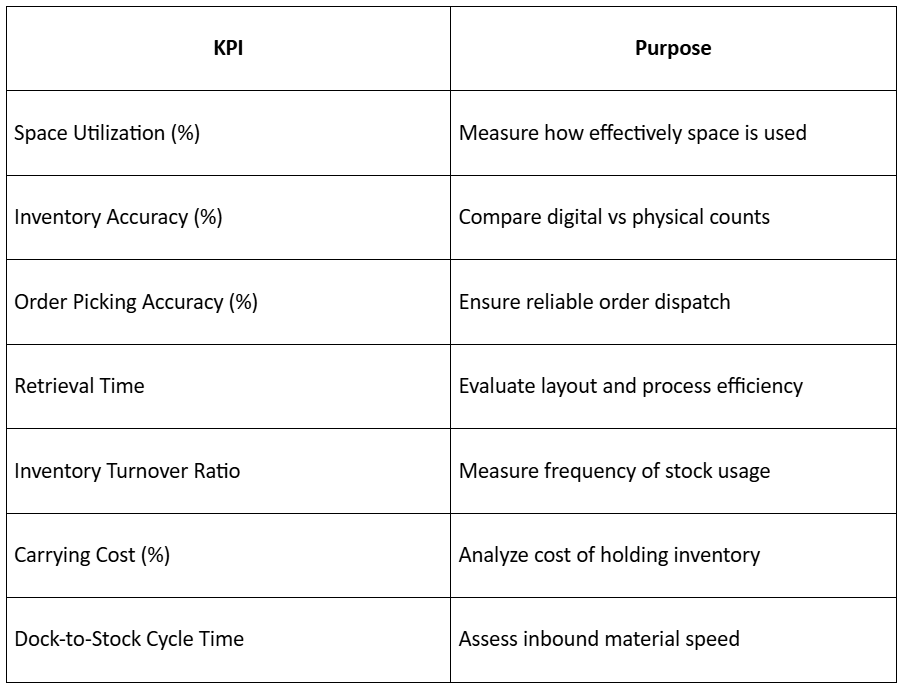
Key Warehouse Performance Metrics (KPIs)
Tracking KPIs helps maintain consistent improvement in warehouse optimization.
Training & Workforce Empowerment
A smart system only works with well-trained staff.
Train teams to:
- Use WMS and scanning devices
- Follow safety procedures
- Suggest layout improvements
- Adopt a Kaizen culture for continuous improvement
An empowered workforce sustains warehouse efficiency long-term.
The Future of Warehouse Space Management
Future-ready warehouses will feature AI-driven optimization, digital twins, and autonomous drones for auditing and tracking.
Next-gen smart warehouses will:
- Predict demand with AI
- Use robotic fleets for fast picking
- Operate with green, energy-efficient systems
- Integrate blockchain for transparent supply chains
Early adopters will achieve faster fulfillment, lower costs, and near-perfect accuracy.
Conclusion: From Storage to Strategic Efficiency
Warehouse space management is no longer a support task — it’s a strategic growth driver.
By combining layout optimization, real-time visibility, and data-driven decisions, businesses can reduce waste, boost productivity, and enhance profitability.
An optimized warehouse doesn’t just store — it powers performance, precision, and progress.
FAQs
Q1. What is warehouse space management?
Warehouse space management involves organizing and optimizing storage areas, layouts, and inventory systems to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Q2. How does a WMS help in warehouse optimization?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) automates tracking, space allocation, and stock movement, ensuring higher accuracy and better visibility.
Q3. Why is inventory turnover important?
High inventory turnover means materials move quickly, improving cash flow and reducing holding costs.
Q4. What technologies are used in smart warehouses?
Smart warehouses use IoT sensors, robotics, AI-driven analytics, and digital twins to enhance productivity and precision.



